How to do Scrum with Kanban
Kanban helps with reducing waste and the scrum can be improved if we use scrum with Kanban to make the teams more efficient. Scrum with Kanban is better, as Kanban brings in features that improve the flow, it not only improves the product but also improves the development process.

The key things that differentiate Scrum and Kanban:
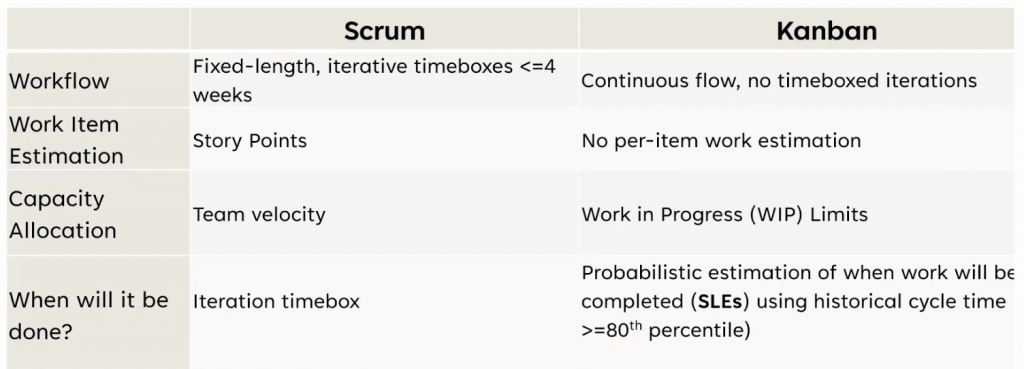
The following Kanban concepts can be added to Scrum to improve team efficiency:
Limit WIP
Set a limit on the amount of work that will be in progress at a time. Do not start any additional work until some of the work has finished to add more work to the system. It can help reduce the added cost of juggling multiple tasks. Also with less work in progress, there will be less context switching, which will make the team more efficient and less stressed.
There is no formula of setting the WIP limit. Some people set the limit by person, each person in the team for example can’t have more than 2 items in progress. Some people put it on the columns, and another way of putting WIP limit is to have an agreement with the team at at a time we will not have more than say 5 stories in progress, so no one will start the 6th story and will wait till one of the 5 stories is done to bring in the next story.

Following the rule of stop starting and start finishing helps focus on the work that has already started. Doing multiple things at the same time may give the feeling of being efficient but it is just a feeling. If the team focuses on a limited amount of work at a time, they will be able to deliver value quickly, receive earlier feedback and learn quicker, so less waste of time doing something which should not be worked on in a certain way.
The quality of the deliverable also improves with focus and having WIP limits helps with getting better at forecasting and managing expectations. There will be more consistency in the cycle time so setting the service level expectation will be easy.
Handling defects
If any defects are identified, fix them in the sprint instead of delaying till the next sprint or adding the defects to the backlog to handle later in future. The longer you wait to fix the defects it will take more time to get it fixed. Do not consider a story to be done, until all the defects identified by the QA are fixed. The developer does not start work on any new story till the defect is fixed.
Simple sizing
Simplify the way we size the work. Instead of using the Fabonacci series, use small medium or large or 1 for small, 2 for medium and 3 for large. There will be lesser numbers to choose from and sizing will be quicker. Another idea is not to size at all as for the teams doing scrum for long time approximately finish the same number of stories in a sprint. Use that number and bring that many stories in a sprint. Kanban team looks at the average throughout to decide how many stories team can work on in a sprint. To ensure that story size is not very large ask the question that can team work on it in e.g. 5 days (half a sprint, so that if there are any defects they can be taken care of within the sprint). If team thinks yes than size is good otherwise split the story can that it can be finished in the certain time frame. With simplified sizing team can use their time more efficiently.
Focus on work
Do not focus on the people but focus on the work.
- Standup: In scrum’s daily standup team typically answer the three questions, and if feels like the status update. The status should be visible on the board and is not needed on daily basis. Also in standup everyone is thinking about the three questions they will have to answer instead of listening to what their team member is strugging with. It helps with collaboration when we are focused on the work and focusing on the work in progress, ask questions like this task is waiting for 5 days what can we do to get it to next stage? or What should we do to unblock this item etc.
- Retrospective: There are multiple ways to run retrospectives but in Kanban, teams look at the work that was completed, notice what took more time than SLE, and work together to find process improvements to avoid that issue again. Now when doing scrum with Kanban, use the similar process. In scrum, no work item should take more than a sprint to finish the work, so at the end of the sprint if there are stories that took more than a sprint to finish, discuss that in retrospective.
CFD
Utilize the CFD to see how the work is flowing during the sprint. If the area of any of the banks is bigger than others that means there is a potential of blocker there. Ideal CFD is having a consistent flow of work so if each band is almost the same size that means that work is flowing consistently. In scrum, there will be steps in CFD due to the start and end of the sprint.
Processes
Evolve the processes incrementally, in the same way as the work is done in iterations.
Visualization of work
Visualize the sprint work in the way work flows which will help identify the issues and wastage in the system and the team can work on it to remove the waste to make them more efficient.
These are some of the suggestions for using the Scrum framework with Kanban to reap the benefits of both.